
The Siberian tiger (panther tigris altaica), also called Ussuri or Amur is one of the subspecies of tigers and is currently considered as the largest cat in the whole world with a size ranging from 7 to 12 feet when full grown. This makes them larger than another huge tiger species, the Bengal tigers. They also weigh around 200 to 770 pounds. Tigers are used to be found in Central and Western Asia. Right now, Siberian Tigers are one of the world’s most endangered species. Here, we list Siberian Tiger facts that would show how close to being extinct they are now.
Siberian tigers are already extinct in most of their original habitat.
Siberian tigers, as mentioned earlier, were used to be found in Central and Western Asia. But those facts do not remain to be true at present. Over the years, Siberian tigers faced conflicts with humans and environment from those locations. And right now, they can only be found in eastern Russia, North Korea and China.
They are genetically close to extinct species.

Scientists found that Siberian tigers have very close genetic makeup with those tiger species that are already extinct. Inbreeding seems to be an impossible method to increase the number of Siberian tigers as this would only result to genetically-poor breed that would not even be fit for survival. Some conclusions have been made that the Siberian tigers will have to face the same faith – extinction.
They now live in isolated areas.
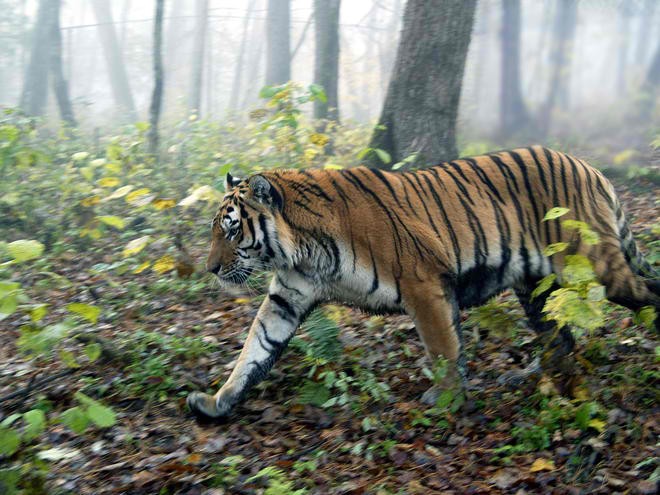

Siberian tigers are now living in the highest mountain areas isolated from any humans. Most of the Siberian tigers that lived in lower parts of the mountains were killed by humans by either hunting them or destroying the forests where they live.
Food hunting becomes harder for Siberian tigers.

Since Siberian tigers tend to live on the highest parts of the mountain for survival, it also became a hard hunting ground to prey. Food supplies for these tigers are now inadequate due to the fact that they can only hunt for few species that live on the same a thick forest areas as they are which includes mostly wild boars and deer.
The myth that they prey on humans.

There are some accounts that would say that Siberian tigers attack and prey on and attack humans. This myth has already been debunked and although they these tigers are carnivores, they do not prey on humans but on wild animals. These tigers are also pretty quick runners for their big size. They can run as fast as 60mph which makes them powerful and strong. And although most people would consider them as intimidating, some find them very challenging. And with that, they attract hunters that want thrill and some trophy of bragging rights killing them.
Hunting them never stops.
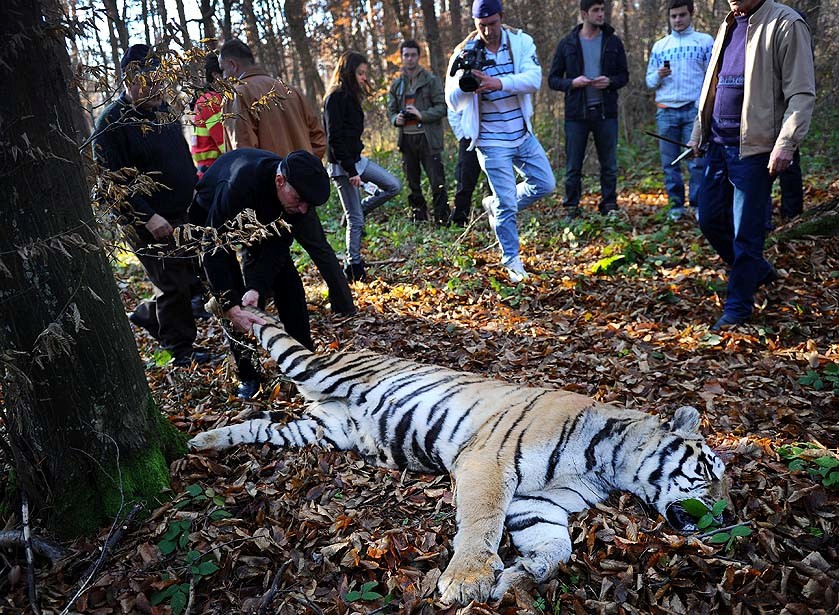

Hunting and poaching Siberian tigers are an endless battle and it will always be an issue. Since these endangered species live in the most isolated areas, there is not enough protection and safety that could be provided for them. Right now, it seems impossible to keep hunters from killing them.
Breeding in captivity.

Although breeding Siberian tigers in captivity pretty works well to increase their numbers, the problem is the quality of offspring it produces. This means that preserving their good Siberian genes is still a hard chore for experts. However, Siberian tigers remain to be the most extensively bred tigers in the world and has the longest running survival plan for any existing tiger species.
Efforts to conserve them proved to be not enough.

Efforts have been made to conserve the remaining Siberian tigers in the world. Russia and China have made researches, campaigns and projects to enhance the conservation of this species that indicated success. However, these efforts proved to be insufficient in fully preserving the still decreasing number of Siberian tigers in the wild.
Female Siberian tigers only produce five cubs.
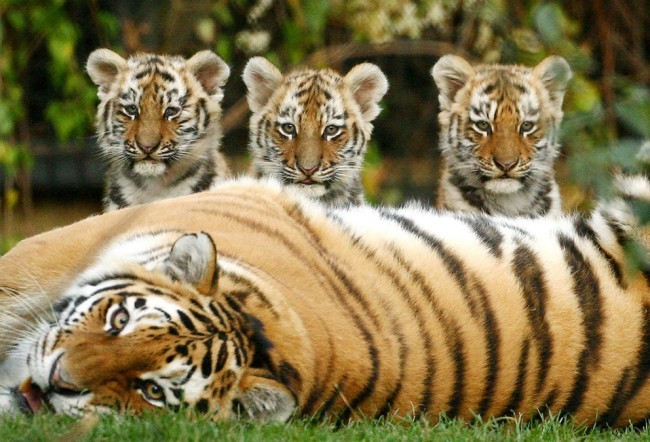

Female Siberian tigers only give birth to five cubs after a gestation period of four months. These cubs will have to feed from their mother for 18 months before they prey by themselves. Although these numbers seem pretty good to increase their numbers, cubs also experience the ‘survival of the fittest’ test when launched to the wild as other large animals can prey on them.
There are only 500 Siberian tigers left in the world.

One of the most alarming of all Siberian tiger facts is their number. Right now, there are only 400 to 500 Siberian tigers existing in the wild. And although research shows that their numbers are pretty stable, these powerful tigers remain to be on the brink of extinction.
Although it is going to take a lot more action to save Siberian tigers from extinction, our own little contributions such as not hunting them or stopping someone from doing so would help a lot. Let us all cross our fingers for these wonderful creatures and hope they won’t come to an end.

